Blockchain technology is revolutionizing the world with its numerous qualities. The technology, along with its multiple projects, has gathered quite some limelight.
Most of these projects promise interesting use cases. However, the real challenge of these projects is mass adoption.
Some basic questions which can influence the adoption of an end-user include:
- How fast can a transaction be processed?
- What will be the response time?
- Can the product be scalable if required?
These questions are still unanswered (or answered in fragments). Blockchain along with its projects are still very much in the early research stage. Multiple projects are trying to answer these questions using differing solution models. We can rely upon these projects to provide us with answers to these questions.
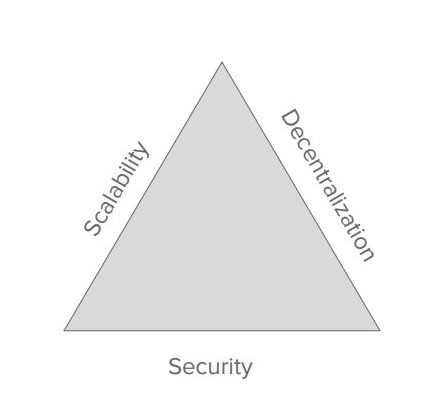
The Blockchain Trilemma
In one of his presentations, Vitalik Buterin demonstrated the Scalability Triangle.
Any high performing Blockchain needs to have 3 major properties. Decentralization, Security and Scalability.
- Decentralization is the essence of Satoshi Nakamoto’s vision. It ensures that there is no central authority to control, thereby making the system fairer and more secure.
- Security: Security is a Blockchain’s capability to defend itself against external attacks. Trying to hack a decentralized Blockchain requires high computing powers and is not cost-effective, the hacker needs to access every instance running in multiple computers. The more decentralized a Blockchain is, the more secure it is.
- Scalability: Scalability is the speed with which the Blockchain processes transactions. Existing Blockchains need to scale up massively to have actual real-life applications.
Now, here is the problem. Existing Blockchain systems can have at most two of the three essential properties mentioned in Vitalik’s Scalability Triangle! This is The Blockchain Trilemma.
Can Blockchain Technology be scalable?
The answer to the scalability is Yes. The question is, how? Through scaling solutions.
Currently, Bitcoin can process approximately 7 transactions per second whereas Visa and Mastercard can process thousands of transactions per second. It will take a huge leap for Bitcoin to be considered as a method of transfer of value. Some solutions need to be introduced to enhance its capabilities.
Bitcoin (BTC) and Ethereum (ETH) were designed to keep decentralization and network security as a priority. As a result, both blockchains have incredibly slow processing speeds.
Balancing scalability, decentralization and network security is the trick which we need to Master.
There are generally four categories of blockchain scaling solutions:-
- Layer 1: on-chain solutions
- Layer 2: off-chain solutions
- Other consensus mechanisms
- Other Distributed ledgers
-
LAYER 1 (ON-CHAIN SOLUTIONS)
Requires changes in the actual codebase of the blockchain. This is difficult to implement and also needs consensus to do so. There are generally 3 popular on-chain scaling solutions:
-
SEGREGATED WITNESS (SEGWIT)`
Transaction signatures take up a huge volume (65%) inside a block. SegWit removes the data attached to a signature by stripping off the signature from within the input. The signatures are moved to a structure towards the end of a transaction. This increases the block size limit on a blockchain (from 1 MB limit for block sizes to a little under 4 MB).
Segregate means to separate, and Witnesses are the transaction signatures. Hence, Segregated Witness, in short, means to separate transaction signatures.
-
SHARDING
Sharding is an On Chain scaling solution. It splits the Blockchain across shards and each node manages its shard (which is only a part of the data on the Blockchain). Each node is responsible for processing its transactions. This makes the network faster.
Some of the benefits of Proof of Stake (PoS) which are favorable to implement Sharding are:
- Designated nodes validate the transactions.
- High staking means high loyalty, thereby maintaining security.
- The Blockchain could be sharded among such stakes. This increases speed and efficiency.
Read our previous article on Sharding
-
HARD FORK
There are situations when a group of people does not agree on certain things with the core community. They decide to part-away by doing structural changes to the underlying code base and create another coin. It results in Hard Forks, where the user base needs to move into a new and improved chain. There is where community consensus becomes all the more important.
Some of the examples are:-
- Bitcoin Cash
- Bitcoin SV
- Ethereum (from Ethereum Classic)
- Litecoin
- DASH
-
LAYER-2 SOLUTIONS (OFF-CHAIN)
These sets of the solution are built on the top of the main blockchain where transactions are ‘off-loaded’ from the main blockchain to save space and reduce network congestion.
-
LIGHTNING NETWORK
This second-layer scaling solution for Bitcoin supports smart contract functionalities on top of Bitcoin’s blockchain, allowing for the creation of private, off-chain channels to support instant transactions with minimal fees. This network tries to lighten the main blockchain by moving the transactions off the main chain (also called ‘off-chain’), and thus reducing the congestion on the blockchain itself.
Read our article on Lightning Network
-
RAIDEN NETWORK
This scaling solution is for the Ethereum blockchain where the users establish private channels (called ‘State Channels’) without broadcasting them to the main blockchain. Raiden is Ethereum’s version of Bitcoin’s Lightning Network.
-
PLASMA
Plasma is another off-chain scaling solution for the Ethereum blockchain where ‘child chains’ that originates from the main blockchain (parent blockchain) functions as separate blockchain transactions but still rely on the main chain for security. Each child chain operates independently and runs parallel thus speed and efficiency are optimized. Also, each child chain can have its own set of rules and qualities.
-
TRINITY
This scalability solution is based on the NEO blockchain. It is similar to Lightning Network and Raiden Network. Trinity uses state channels to increase blockchain throughput, focusing on real-time payments, privacy protection and low fees for NEO assets.
-
SCALABLE CONSENSUS MECHANISM
To achieve greater scalability and transaction processing several consensus mechanisms streamlines the consensus-making process.
-
DELEGATED PROOF-OF-STAKE
Here the token holders vote in delegates that validate transactions on the network on their behalf. The number of voted delegates can range anywhere from 10-100 depending on the system and are periodically changed. Delegates that do not perform well or harms the system will be voted out by token holders and replaced. DPOS is partially centralized and can run faster than other traditional public blockchains.
- Steemit
- EOS
- Bitshares
- Ark
- Lisk
-
BYZANTINE FAULT TOLERANCE (BFT)
This is the property of a distributed system where the system is constantly achieving consensus even if there are adversarial actors within the network. This means that a BFT system can continue operating even if some of the nodes fail or act maliciously.
-
OTHER SCALABLE DISTRIBUTED LEDGERS
These distributed ledgers do not organize information (transactions) into chained, sequential blocks. They are not Blockchain. The most popular ones include IOTA and Hedera Hashgraph. IOTA uses a technology called Tangle and Hedera Hashgraph uses one called Hashgraph. The purpose of these systems remains the same. Create an immutable Ledger that is scalable, secure and decentralized.
Source: Master The Crypto, Investopedia Segwit