Ethereum is about to make the long-awaited change from PoW to PoS. Instead of the standard, “it will be another 6 months”, the change seems more imminent. This will bring many changes to the Ethereum network and ecosystem.
We all look forward to less congestion and cheaper transactions on Ethereum. In this article, we like to focus on the network being faster again. That is all about the TPS or transactions per second. Ethereum wants to achieve this by sharding.
Now, Vitalik Buterin has his blog and he recently wrote an interesting post. It covers sharding and where it will bring the Ethereum network. Let’s take a look at what he has to say.
What Is Sharding?
Sharding is when you break larger chunks of data up into smaller chunks. You break up a database, with lots of information, into smaller parts. This makes your network faster, and it is easier to manage.
Let’s give an easy-to-understand real-life sample. That is always the best way to show you what it means: You are in a big store at the cashier, it’s busy and only one cashier is at work. It will take a while before you can pay for your goodies and leave. Now, imagine the same situation. However, the store opens up a few more cashiers. As a result, all the queues at the cashiers disappear. Everybody can pay for their goods and leave quickly. That is kind of how sharding works.
Sharding and the Blockchain Trilemma
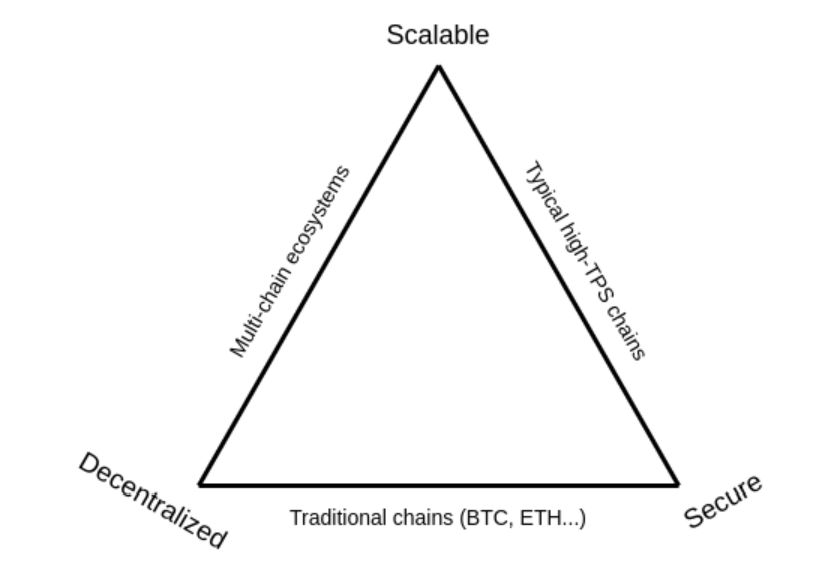
So, sharding is going to benefit the Ethereum network. Before we can show this, let’s look at something else first. That is the blockchain trilemma. This trilemma says that each blockchain has 3 properties. These are scalability, decentralization, and security. However, from these 3 properties, only 2 work in every blockchain.
Source: Vitalik Buterin’s blog
A few projects claim to have solved the trilemma. Instead, let’s have a look at all blockchains that couldn’t solve it.
- Traditional blockchains—Think Bitcoin or Litecoin or other PoW chains. They managed decentralization and security. However, they are not scalable.
- High-TPS chains—These are scalable and secure. Unfortunately, they lack decentralization.
- Multichain ecosystems—They handled the decentralization and scalability part. But they lack security.
On the other hand, sharding covers all three parts of the trilemma.
- Scalability—It can process many transactions. More than a single node, like Bitcoin.
- Decentralization—It can run on your laptop or pc.
- Security—It’s not possible to single out a part for an attack. You can only attack the whole system.
Sharding Options, the Vitalik Way
One of the ways Vitalik describes sharding is by random sampling. He also mentions that Ethereum uses stronger trust properties for its sharding. However, random sampling is easier to explain.
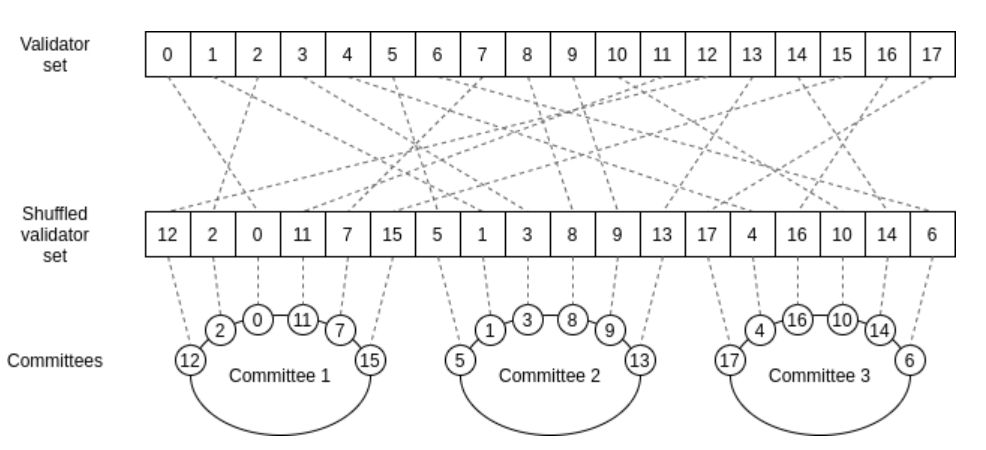
The sample is a PoS chain that has many validators, up to 10,000. Furthermore, there are 100 blocks to verify. There is simply no computer powerful enough to do this. A new set of blocks would come in before the validators could verify the previous 100 blocks.
The solution is to randomly shuffle the validators and split up the work. You make groups of 100 validators, and each group verifies a new block. Group 1 verifies a block, now group 2 verifies the next block, etc. We call such a randomly shuffled group a committee.
Source: Vitalik Buterin’s blog
Each validator that verified a block, signs this off with a signature. As a result, all other validators, don’t need to verify 100 blocks, but only the 10,000 signatures. This is a lot less work.
In turn, this leads to the computing power of each node increasing by 2x. As a result, each node can validate twice as many signatures. Now you can have 200 committees instead of just 100. This means that you can also verify 200 blocks instead of 100. What is interesting, is that each block can now double in size. In short, you have 2 x more blocks that are twice the size. That improves chain capacity by 4x.
What Is the Difference Between Sharding and Partitioning?
Both sharding and partitioning want to achieve the same thing. When you have a large set of data, break it up into smaller parts. However, both take a different approach.
Sharding looks at it from a perspective that you can find all the data on a variety of computers. On the other hand, partitioning looks at it by grouping all data of the subsets into a single database.
Similar, but at the same time, very different. Blockchains use sharding over partitioning. The reason seems obvious! Because blockchains connect to many computers.
Conclusion
So, the short answer to the title of this article is ‘yes’. Sharding will make Ethereum’s TPS rate a lot better? We showed you how sharding solves the blockchain trilemma.
Furthermore, there’s also an explanation of how Ethereum wants to use sharding. At last, we looked at the difference between sharding and partitioning. Now, Vitalik, bring it on and let the games begin. We are all eagerly awaiting the change to PoS.
⬆️ Also, get $125 for SIGNING UP with MEXC Exchange (FREE $25 in your MEXC wallet + 1-month ALTCOIN BUZZ ACCESS PRO membership (worth $99). MEXC supports U.S. Traders in all trading pairs and services.
(To get your ALTCOIN BUZZ ACCESS PRO membership, DM us with your “newly signed up MEXC UID” and “Telegram ID” on our Twitter @altcoinbuzzio)
⬆️In addition, find the most undervalued gems, up-to-date research and NFT buys with Altcoin Buzz Access. Join us for $99 per month now.
⬆️Finally, for more cryptocurrency news, check out the Altcoin Buzz YouTube channel.