The future of blockchain is about interoperability. This is also known as cross-chain. It means that two different blockchains can speak with each other. This feature will make the crypto space go around.
The easier cross-chain between two or more blockchains is, the more the blockchain space can grow. So, let’s have a look at how this works.
⛓️ @THORChain opens the doors to cross-chain swaps from #Avalanche to seven other chains
🌉 BridgeSwap will allow users to execute those cross-chain swaps directly from Pangolin’s user interface…https://t.co/HyMh3Pk4cv
— Pangolin 🔺☀️ (@pangolindex) October 23, 2022
What Is Cross-Chain in Blockchain?
Each blockchain uses its own language. They are also all coded differently. In other words, they can’t talk to each other. However, we do need them to talk to each other. There are many reasons for that. For example, transferring digital assets between chains. Either NFTs, coins, or other information.
Cross-chain makes this possible. They make the various blockchains interoperable. As a result, we, as users, can access all these different protocols much easier. For this cross-chain, blockchains use bridges. Currently, that is a weak point. Unfortunately, there are regular hacks on bridges. This is something the crypto community or devs need to work on.
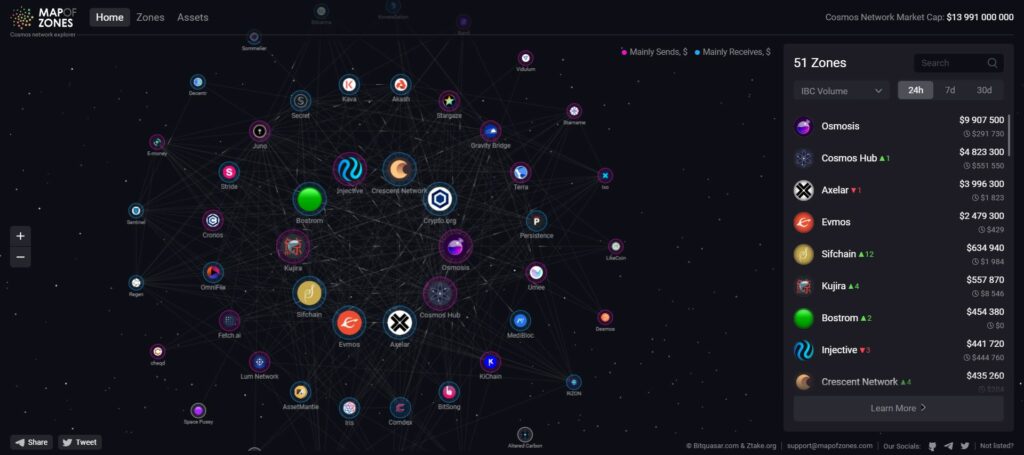
On the other hand, earlier this year, there was GeckoCon 2022. This was an online crypto conference. There were plenty of different discussions. One of them was about the future of interoperability. The panel saw this future as being seamlessly integrated. We, the users, together with the devs, don’t even know what blockchain we’re on. We’ll find ourselves back where the gas costs are low and volume is high. Read our dedicated article about this GeckoCon discussion. In the picture below, you can see a map of the Cosmos zones.
Source: Cosmos map of zones
What Is Cross-Chain DeFi?
DeFi has many exciting options to offer. For example, liquid staking, lending, borrowing, and more. Interoperability will turn out to be crucial for the DeFi space. To make a fist against the CEXs, they will need this interoperability. CEXs are convenient, but they have a centralized set-up. You have no control over your assets. On the other hand, DeFi is all non-custodial.
Some current DeFi protocols that support cross-chain, are, for example:
- Polkadot — Parachains and bridges to other networks like Ethereum.
- Near — The Rainbow bridge between Near and Ethereum.
- Avalanche — Their ecosystem has many interoperable solutions.
- Cardano — In their ecosystem, you can find many interoperable cross-chain solutions.
- XDC — Interoperable smart contracts. These can run with dApps on other blockchains.
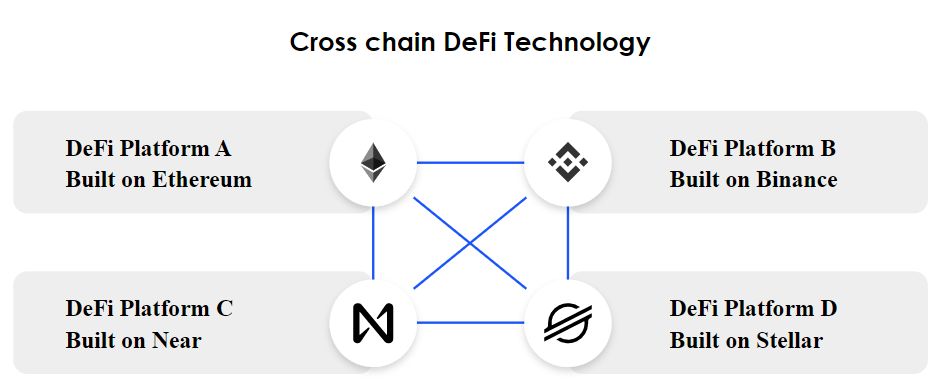
The picture below shows how cross-chain works between DeFi platforms.
Source: Leeway Hertz
How Do Cross-Chain Bridges Work?
A cross-chain bridge allows digital assets to move between different blockchains. These bridges are typically decentralized; they are dApps. The bridges work with smart contracts. So, on the source side, either tokens get burned or locked. On the destination chain, another smart contract waits. This unlocks the tokens or mints new tokens.
So, tokens don’t actually move between blockchains. For example, you want to spend your Bitcoin in the Ethereum ecosystem. What happens is that your Bitcoin gets locked on one side of the bridge. On the other side, you get an equal amount of Ethereum. Now, you spend some Ethereum, and what remains, you send back to Bitcoin. So, the bridge burns the leftover Ethereum tokens. On the Bitcoin side, you receive an equal amount of BTC.
This is the same principle as using PayPal to pay for your online spending. Regardless of what and where you buy it. Or using MasterCard to pay for your Visa bills.
What Is a Cross-Chain Transfer?
A cross-chain transfer is nothing else but a transaction between two blockchains. You send an asset from the originating chain to a different chain.
Besides a bridge, you will also need a wallet. Popular wallets are, for example, MetaMask or Trust Wallet. However, there are plenty of other wallets out there. Some may be useful for a variety of chains. On the other hand, some may only work between two chains.
Occasionally, you need to have two wallets open. For instance, when the receiving wallet doesn’t support MetaMask or Trust Wallet.
You can send Ethereum with MetaMask or Trust Wallet to the L2. However, once your ETH is on the L2, you require a different wallet. On the L2, you have another wallet open at the same time. This allows both wallets to connect through the same platform. Once you complete the transfer, you can use ETH on the L2.
For example, StarkNet is such a case. An airdrop is imminent, and you can find info about the airdrop in this video.
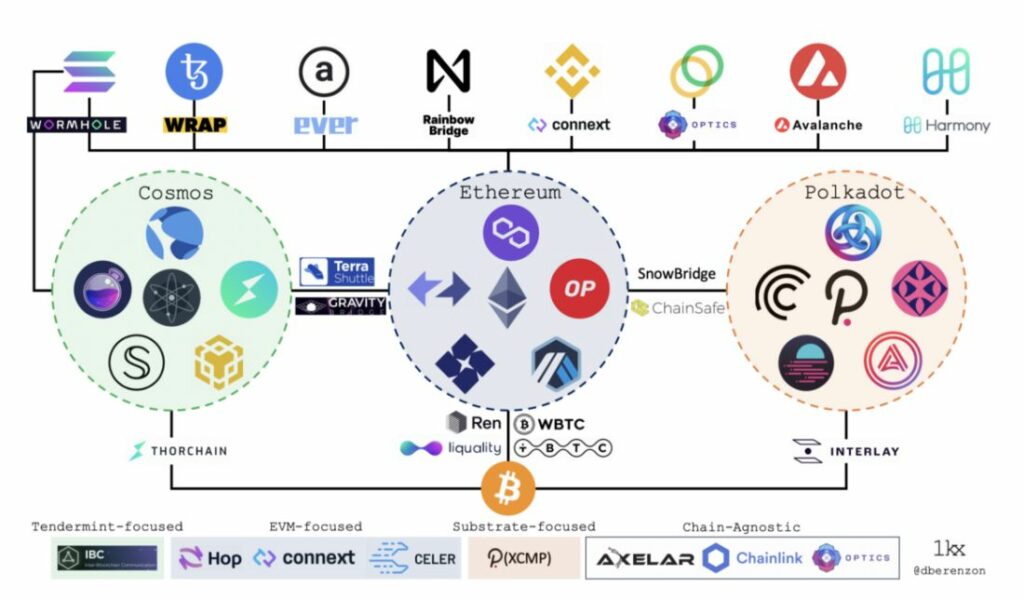
The picture below shows how cross-chain works between a variety of chains. This includes many DeFi platforms.
Source: Medium
Conclusion
Cross-chain and interoperability are important in crypto. They guarantee the growth of the crypto space. With cross-chain bridges, different blockchains can talk to each other. In other words, we can move digital assets around between blockchains. In this article, we answered four common questions about cross chain in crypto.
⬆️For more cryptocurrency news, check out the Altcoin Buzz YouTube channel.
⬆️ Check out our most up-to-date research, NFT and Metaverse buy, and how to protect your portfolio in this market by checking out our Altcoin Buzz Access group. And for a limited time, it’s totally FREE. Just click the link and Try it today.