In “Quick Concepts” we will explain to you, in a simplified format, the important Terms/ Technologies/ Advancements used in the Blockchain space. Today’s topic is the Lightning Network.
Introduction
Previously, in Chapter 1 of Quick Concepts, we discussed the On-Chain Blockchain scaling solution, Sharding. Today we will look into an Off-Chain scaling solution, Bitcoin’s Lightning Network.
Background: A quick recap – The Blockchain Trilemma.
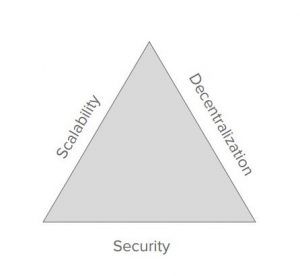
In one of his presentations, Vitalik Buterin demonstrated the Scalability Triangle.
Any high performing Blockchain needs to have 3 major properties. Decentralization, Security and Scalability.
- Decentralization is the essence of Satoshi Nakamoto’s vision. It ensures that there is no central authority to control, thereby making the system fairer and more secure.
- Security: Security is a Blockchain’s capability to defend itself against external attacks. Trying to hack a decentralized Blockchain requires high computing powers and is not cost-effective, the hacker needs to access every instance running in multiple computers. The more decentralized a Blockchain is, the more secure it is.
- Scalability: Scalability is the speed with which the Blockchain processes transactions. Currently, Visa has a transaction speed of 1,700 transactions per second. Bitcoin Blockchain can handle ~3-7 transactions per second, while the Ethereum Blockchain can handle ~12–30 transactions per second. This means the existing Blockchains need to scale up massively to have actual real-life applications.
Now, here is the problem. Existing Blockchain systems can have at most two of the three essential properties mentioned in Vitalik’s Scalability Triangle! This is The Blockchain Trilemma.
Why can’t traditional Proof of Work (PoW) Protocols, like Bitcoin scale?
Traditional PoW protocols like Bitcoin & Ethereum requires all the nodes on the network to store and process all the transactions (the entire Blockchain!). With the exponential increase in network size, maintaining network integrity with bigger Blockchains becomes resource intensive, transaction confirmations take longer which in turn makes the network slow.
Different scaling solutions:
Enterprise-grade Blockchains needs to be secure. Hence, either decentralization or scalability is compromised in existing projects.
In some Blockchains only selected nodes can validate transactions, thereby increasing scalability but compromising on decentralization. The others are not scalable enough.
There is no single and clear solution to handle the scalability problem. Various solutions have been proposed which can be broadly classified as:
The Lightning Network: Concept
Proposed by Thaddeus Dryja and Joseph Poon in a 2015 white paper, the Lightning Network is a new protocol layer built on top of Bitcoin to be used for instant, high-volume micropayments.
The Lightning Network paper demonstrates the characteristics of Lightning Network as below:
- In the Blockchain, if only two participants care about an everyday recurring transaction, it’s not necessary for all other nodes in the bitcoin network to know about that transaction. It is instead preferable to only have the bare minimum of information on the Blockchain. This will reduce the load on the Blockchain.
- Lightning Network opens up Off-Chain micropayment channels, which creates a relationship between two parties. Scalability can be achieved using a large network of micropayment channels.
- It is possible to create a near-infinite amount of transactions inside this network, using this concept.
- The obligation to deliver funds to an end-recipient is achieved through a process of chained delegation. Each participant along the path assumes the obligation to deliver to a particular recipient. Each participant passes on this obligation to the next participant in the path. The obligation of each subsequent participant along the path, defined in their respective HTLCs (Hashed Timelock Contract), has a shorter time to complete compared to the prior participant. This way each participant is sure that they will be able to claim funds when the obligation is sent along the path.
- Bitcoin Transaction Scripting, a form of what some call an implementation of “Smart Contracts”, enables systems without trusted custodial clearinghouses or escrow services.
- The contracts are enforced by creating a responsibility for one party to broadcast transactions before or after certain dates.
Lightning Network fees, which differ from Blockchain fees, are paid directly between participants within the channel.
The Lightning Network: Execution Model
Lightning Network is a network of Off-Chain payment channels. The transactions can happen in 2 ways
- Direct Payment between 2 parties
- Indirect Payment Channel between 2 parties
Direct Payment Channel:
- Open a payment channel – The counterparties deposit an amount of Bitcoin in a Multi-signature address which acts as a safe. In case of a purchase, the Purchaser provides all the funding and this is a single-funded channel.
- The initial transaction is broadcasted to the Bitcoin Blockchain.
- The Seller can view this initial transaction (though he has not received the amount yet), which gives him trust and can decide to conduct further transactions with the same Purchaser till the time he desires to end the contract and receive the payment in his Wallet.
- A balance sheet is also created Off-Chain with the balances for both parties recorded.
- If the Purchaser has further balance, he can perform more transactions with the Seller.
- Each time the Balance Sheet gets updated, the transaction amount moves from the Purchaser’s balance to the Seller’s balance.
- Each of these time, the balance sheet is signed with the Purchaser’s and Seller’s private keys, confirming the agreement.
- When one party decides to close the payment channel, the party simply broadcasts the latest balance sheet signed by both parties to the Blockchain network.
- Bitcoin miners will validate the balance sheet signatures and will confirm the release of funds.
Hence the lightning network needs only 2 transactions in the Bitcoin Blockchain,
-
- To open the payment channel (Depositing the Bitcoin), and
- To close the payment channel (Settling the bill).
This significantly reduces the load on the Bitcoin Blockchain.
Indirect Payment channels:
There is no need to create payment channels with everyone. If there is no established channel between a Purchaser and Seller,
- A Seller generates a secret key called preimage, which is hashed and put in an invoice
- The invoice is sent to the Purchaser
- The Purchaser uses the invoice to create a Hashed Timelock Contract (HTLC)
- The purchaser sends the HTLC across a channel within the Lightning Network.
- The immediate recipient cannot claim the amount as he does not have the
- So he creates an HTLC with his own funds (he gets some fee in return).
- The Lightning Network finds the payment channel which is fastest (least amount of intermediates) and cheapest.
- At the end of the channel, the seller uses his own preimage to claim the fund.
Source Wikipedia
A beautiful demonstration is also provided in the following video
Use Cases of Lightning Network
The Lightning Network paper mentions various use cases:
- Instant Transactions. Using Lightning Network, Bitcoin transactions are now nearly instant with any party (direct non-revocable payment in milliseconds to seconds).
- Exchange Arbitrage. There is presently incentive to hold funds on exchanges to be ready for large market moves due to 3-6 block confirmation times. It is possible for the exchange to participate in this network and for clients to move their funds on and off the exchange for orders nearly instantly.
- Micropayments. Bitcoin Blockchain fees are far too high to accept micropayments, especially with the smallest of values. With Lightning Network, near-instant micropayments using Bitcoin without a 3rd party custodian would be possible. It would enable, for example, paying per-megabyte for internet service or per-article to read a newspaper.
- Financial Smart Contracts and Escrow. Possibility to have highly complex transaction contract terms without ever hitting the Blockchain.
- Cross-Chain Payments. Possibility to have transactions to be routed over multiple chains with different consensus rules.
- Privacy. As transactions on Lightning Network are not recorded on the Blockchain users are provided with a more private way of transacting Bitcoin.
Adoption
Lightening Network has received huge support.
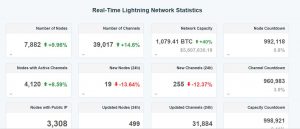
On April 24, 2018, we reported that the Lightning Network has 2027 nodes, 5818 channels, and network capacity of $155 thousand USD.
After almost a year as on April 8, 2019, the Lightning network boasts of 7882 Nodes, 39017 channels and network capacity of $5607 thousand USD.
Source: 1ml
More in-depth details about recent adoption can be found in this article.
Join us on Telegram to receive free trading signals.
For more cryptocurrency news, check out the Altcoin Buzz YouTube channel.