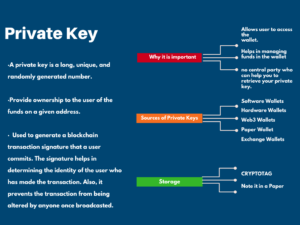
A private key is a random number that grants ownership to the user of the funds on a given address. It generates a signature when a user commits a blockchain transaction. This signature helps in determining the true identity of the user.
The primary goal of blockchain technology is to provide a secure transmission channel without any intermediary. Thus, to achieve security, public cryptography, or encryption technology, is mandatory. This will leverage the users to send/receive data using a secured network without any worry.
The network adds another layer of security to verify and approve the transactions.
Cryptography supports two pairs of keys:
- Public keys: Used for identification and is visible to all users in the network.
- Private keys: Used for authentication and encryption. Users need to keep it safe and secure.
In this article we will focus on the following points:
Why the private key is important for a user to safeguard their assets.
What are the various methods which can help you securely keep your private keys?
A list of Do’s and Don’ts which one should follow.
What is a private key?
- A private key is a long, unique, and randomly generated number.
- Provides ownership to the user of the funds on a given address.
- Used to generate a blockchain transaction signature that a user commits. The signature helps in determining the identity of the user who has made the transaction. It prevents the transaction from being altered by anyone once broadcasted.
Important: The private key is encrypted, i.e., it is not publicly visible. The key authorizes the transaction in the background and none of the participating users in the transaction processing are able to see the private key.
Why it is important to keep your private keys safe
We have always heard a warning to keep your private keys safe. Why it is being said so?
- The private key allows a user to access the wallet.
- It helps in managing funds in the wallet.
- There is no third party who can help you to retrieve your private key.
Sources of private keys
To keep your digital assets, you need wallets. You will get private keys from all the wallets (except centralized exchanges) where you have kept your assets. Currently, different types of crypto wallets are available.
- Software Wallets: These allow access to multiple blockchains. These wallets do not provide an exchange facility (except swaps).
Popular software wallets: Atomic wallet, Trust wallet
- Hardware Wallets: These are physical devices used to store your funds offline. Currently, the hardware wallets are considered as the most secure option.
Popular hardware wallets: Ledger, Trezor, KeepKey
- Web3 Wallets: Web3 wallets serve as an extension of many browsers. It allows you to manage your Ethereum wallet to send/receive funds.
Popular Web3 wallet: Metamask
- Paper Wallet: Keys are printed in QR code form which can be scanned while making transactions.
Popular service provider platform: Bitaddress
- Exchange Wallets: Allows the user to access their funds once connected to the internet from any browser.
Popular exchange wallets: Binance, CoinBase.
In an exchange wallet, users do not have control over their private keys. The platforms hold and control users’ keys.
Storing private keys
- CRYPTOTAG –Crypto tag is getting the limelight nowadays. It is a titanium plate in which the user engraves the hardware wallet’s seed phrase.
The titanium plates are indestructible, thusly helping in keeping the seed phrase safe.
Disadvantages:
-
-
-
- It is not reusable, i.e., you have to buy new plates if you make a mistake while engraving or if there is any change in the wallet’s address.
- It is easily identifiable.
-
-
- Note it on a paper: You can write your keys on a piece of paper. It is your responsibility to keep the paper safe.
Disadvantages:
-
-
-
- The paper can be damaged or lost.
- Other people can gain access to it and see your private key.
- To retain it for a longer period of time, you can laminate the paper and put it in your bank locker. But still, this method cannot protect the paper forever. Also, keeping in a bank locker is risky.
-
-
Do and Don’ts
Are the 12-word backup phrase and private key the same?
A wallet setup generates a 12-word backup phrase known as a seed phrase. This is different from the private key as it encapsulates the private key into a format understandable by humans. That means it converts a string of alphanumeric into a string of 12 random dictionary words.
The backup phrase restores your assets. So, in case if you lose your backup phrase, you will also lose access to your private keys and digital assets.
Conclusion
The private key gives you access to the wallets and funds. No matter what type of wallets you are using, if you are holding assets, you have to be responsible to keep the keys safe and secured. Otherwise, you will lose access to all your funds. The private key is not maintained by any third party that you can call and ask for help if lost. It is the user’s primary responsibility to keep it safe.